Linux 内核select、poll 和 eventpoll 的实现
Linux 内核仓库 https://github.com/torvalds/linux
Linux 内核文档: https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/index.html( 中文)
开发工具参考: https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/dev-tools/index.html
也可以使用 VSCode + 插件C/C++ GNU Global
通过前面三个博客可以得知 select,** poll, eventpoll** 的详细实现,现在来总结对比下它们之间的不同:
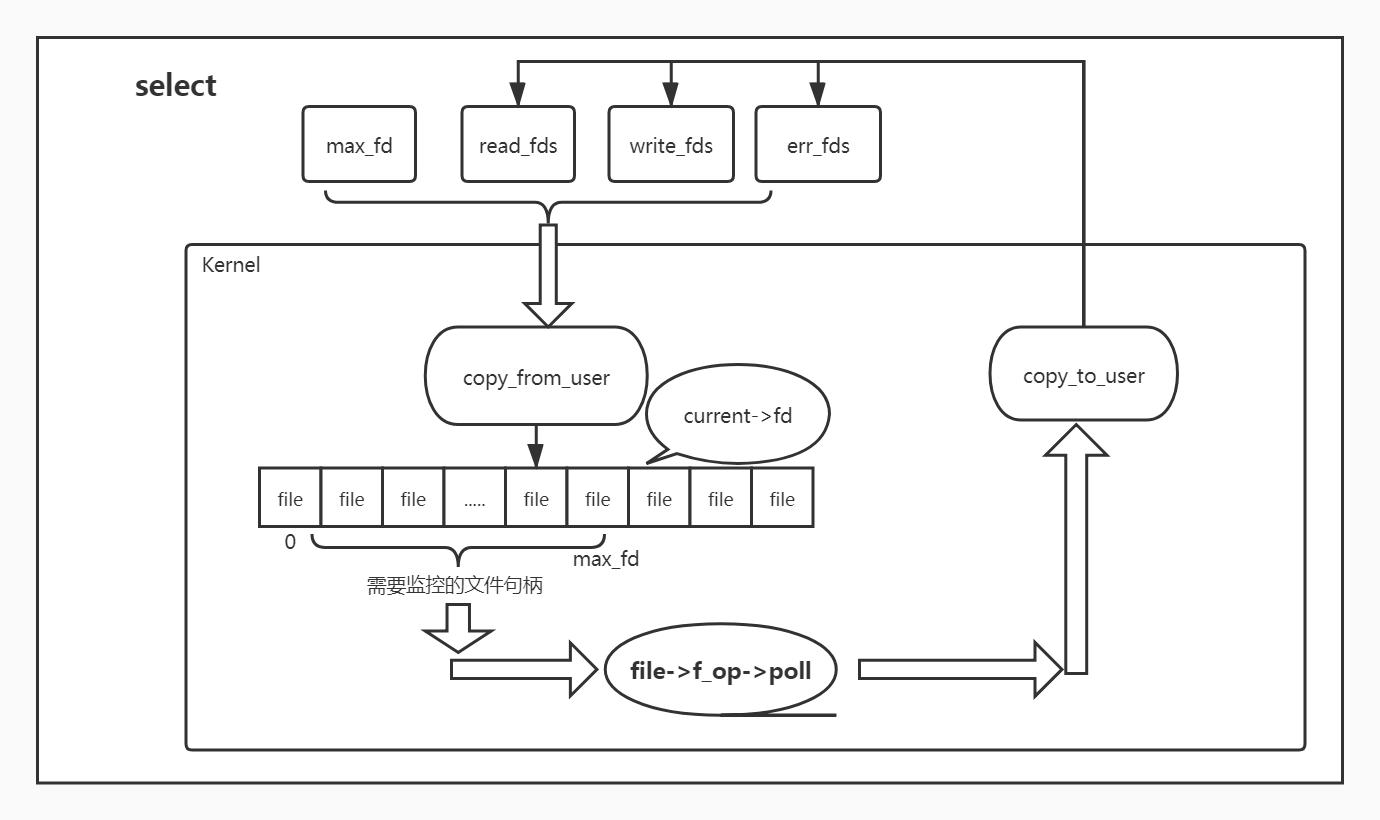
- select 流程图
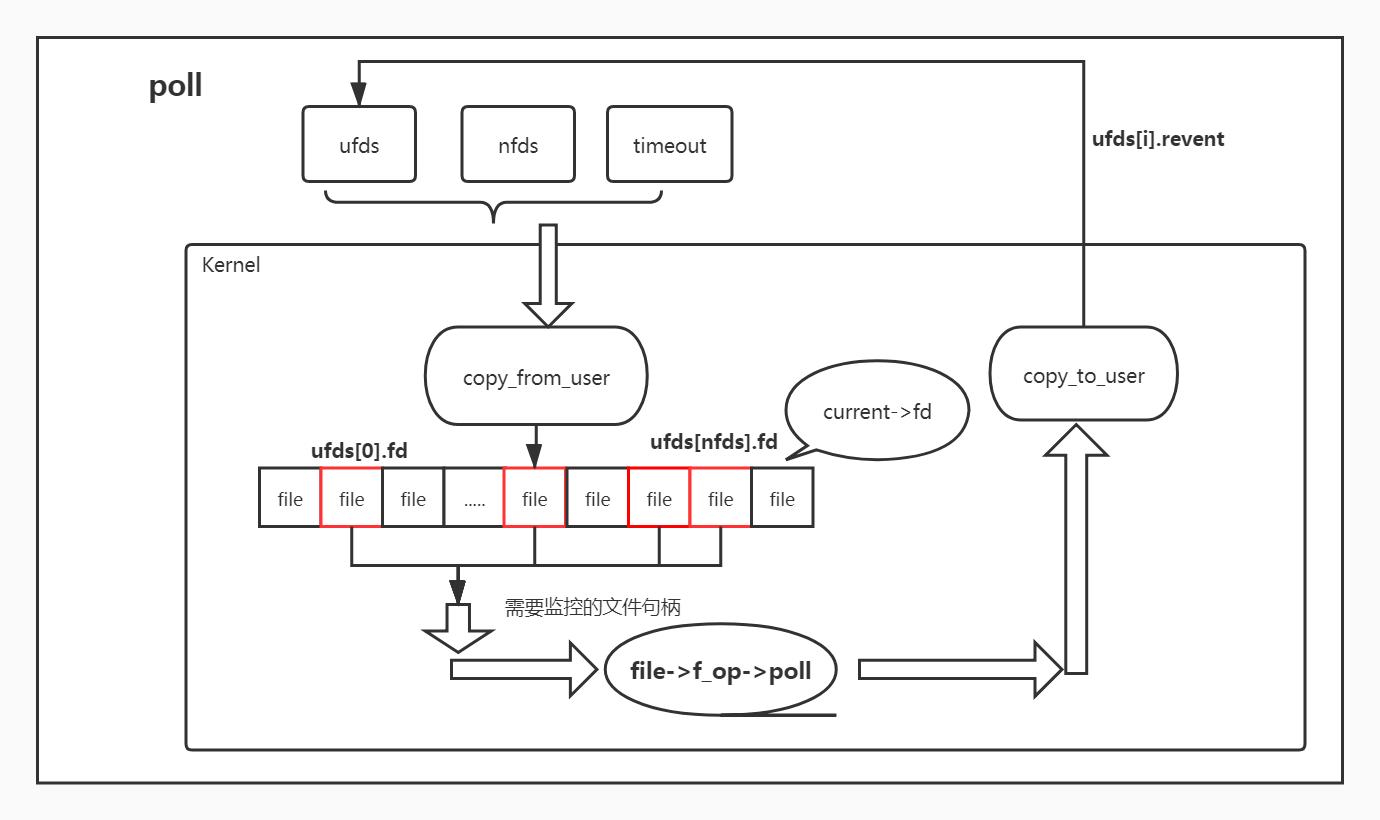
- poll 流程图
- eventpoll 流程图
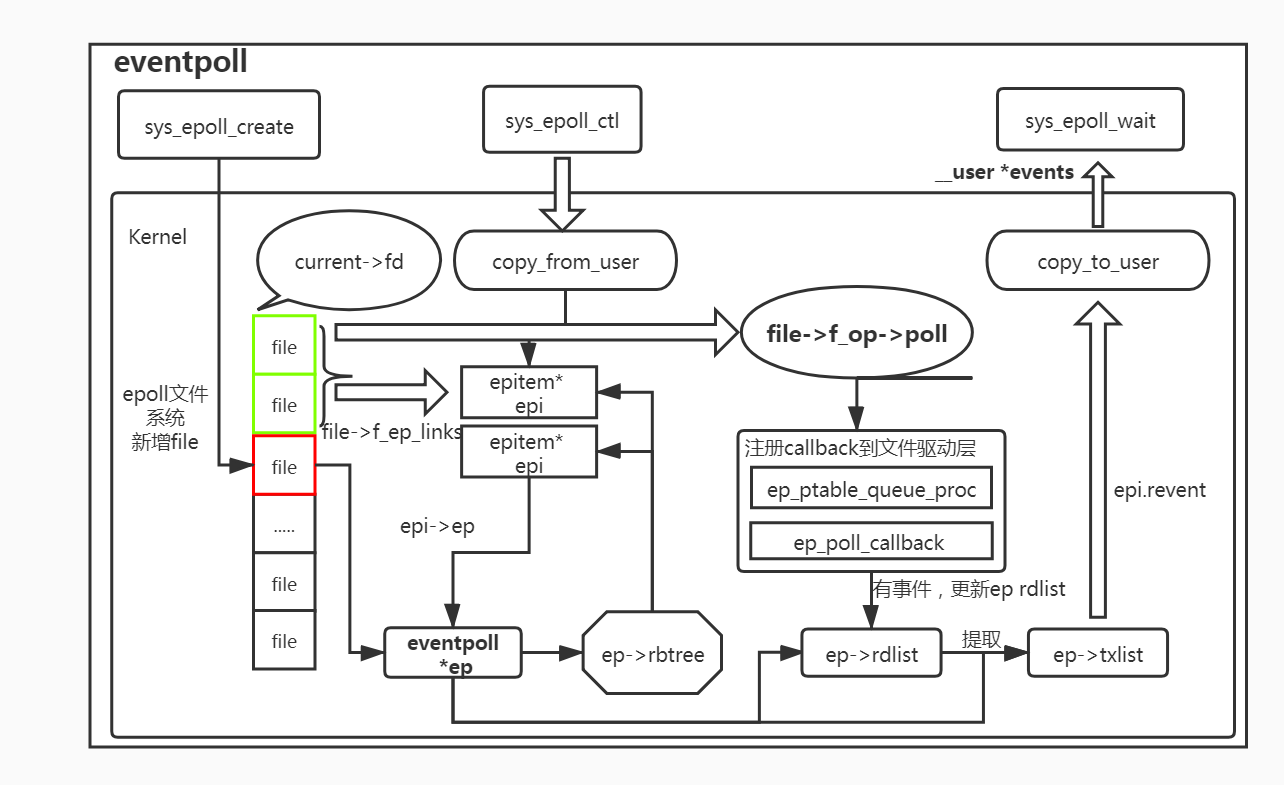
- 优缺点总结 <1> 监控文件最大数不同:select和poll都是以数组形式传入药监控的文件句柄,而这个数组是有大小限制的1024个左右(不是很清楚).而epoll则是每add一个文件句柄会new一个新epi出来,挂载在ep的红黑树中,监控的文件个数没有明确限制(可能会受限于系统最大打开文件句柄数)从这点上看,epoll是优于select和poll. <2> copy参数次数不同:无论是select/poll/epoll都是有对应的系统调用,其参数都会从userspace拷贝到kernelspace,如果监控的文件句柄数很大,select/poll在这方面的耗时会明显多于epoll,因为每次调用select/poll都要重新拷贝一次所有的监控句柄,而epoll则在sys_epoll_ctrl的时候添加一次存储在内核数据结构中,后续的sys_epoll_wait会通过内核数据找到监控的文件句柄对应的file和监控得到的event. <3> 轮询方式的差异:select 会传入监控句柄的最大句柄,从而监控查询0 ~~ max_fd之间的所有file的驱动状态来获取想要的文件句柄中想要的event,而poll则只会轮询用户传入的文件句柄集,相比select会少轮询很多file的状态,这点上poll明显优于select.而epoll则是完全异步的方式,哪个有更新会添加到ep->rdlist中,epoll_wait来取走.当连接数不是很多且每个client都非常活跃的情况下,poll > select > epoll,而当连接数巨大且大多数client都是潜水状态的情况下,epoll > poll > select。
本文摘自: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38537730/article/details/104100468
By admin
read more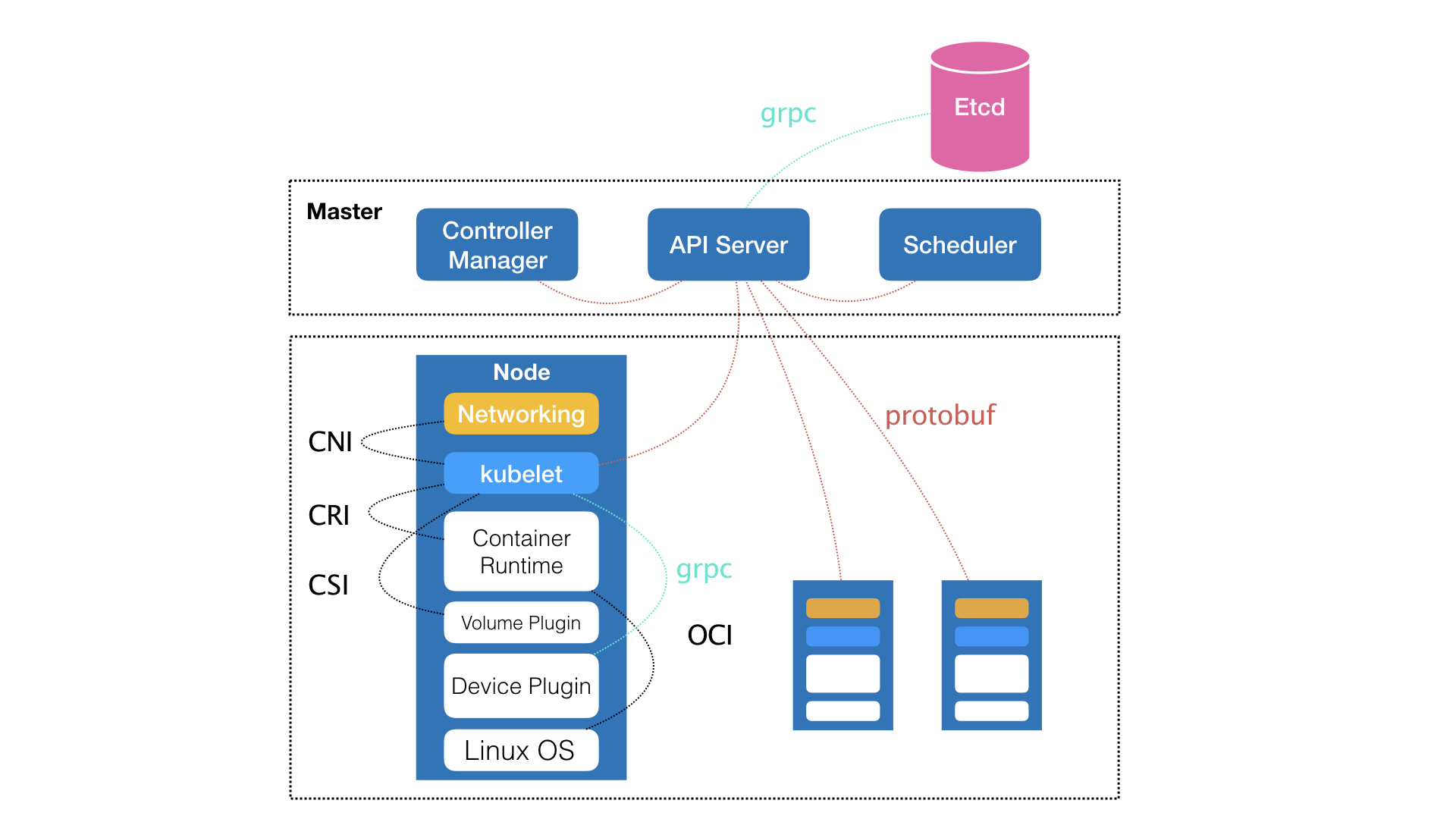 kubernetes 架构图
kubernetes 架构图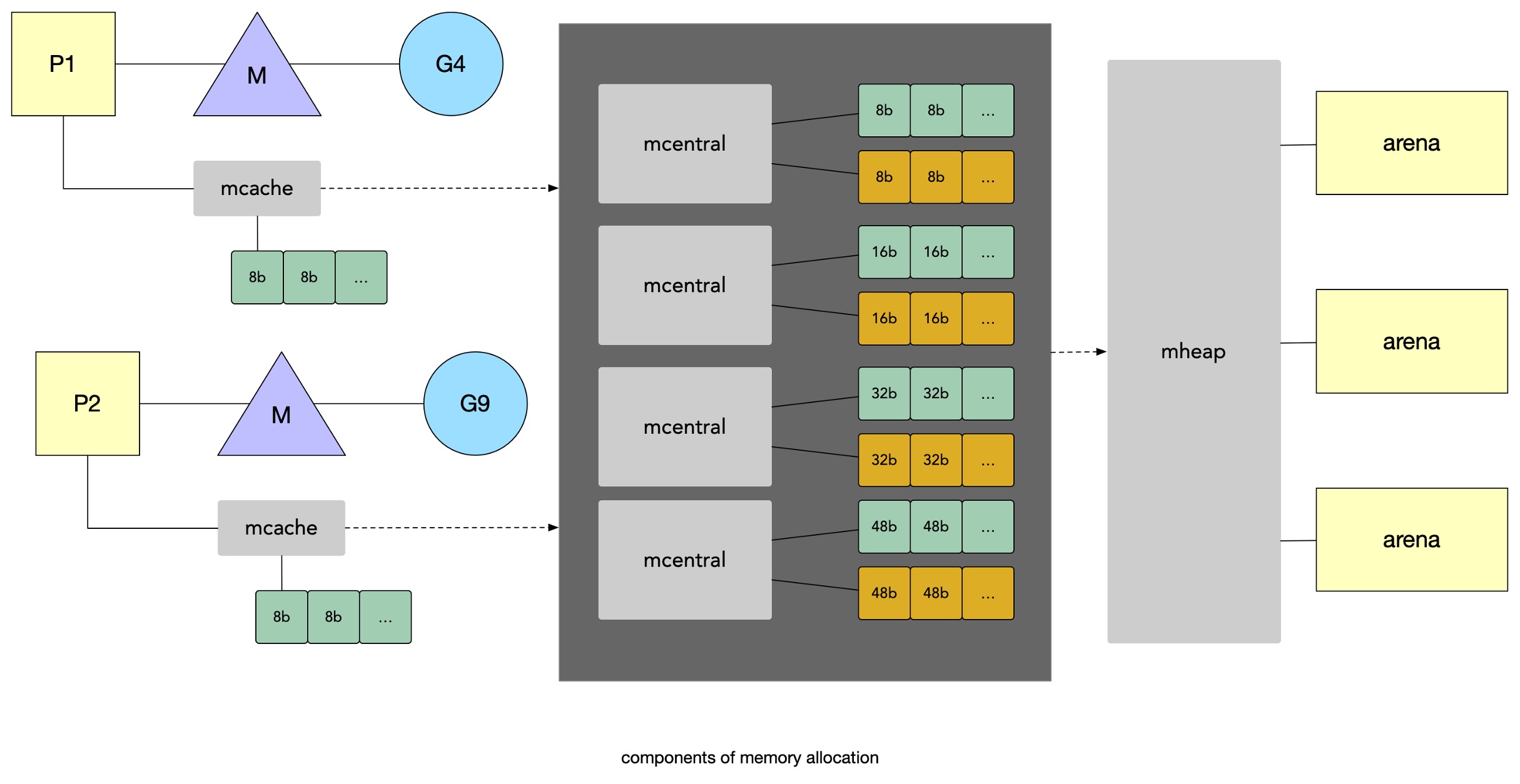 golang 内存分配组件
golang 内存分配组件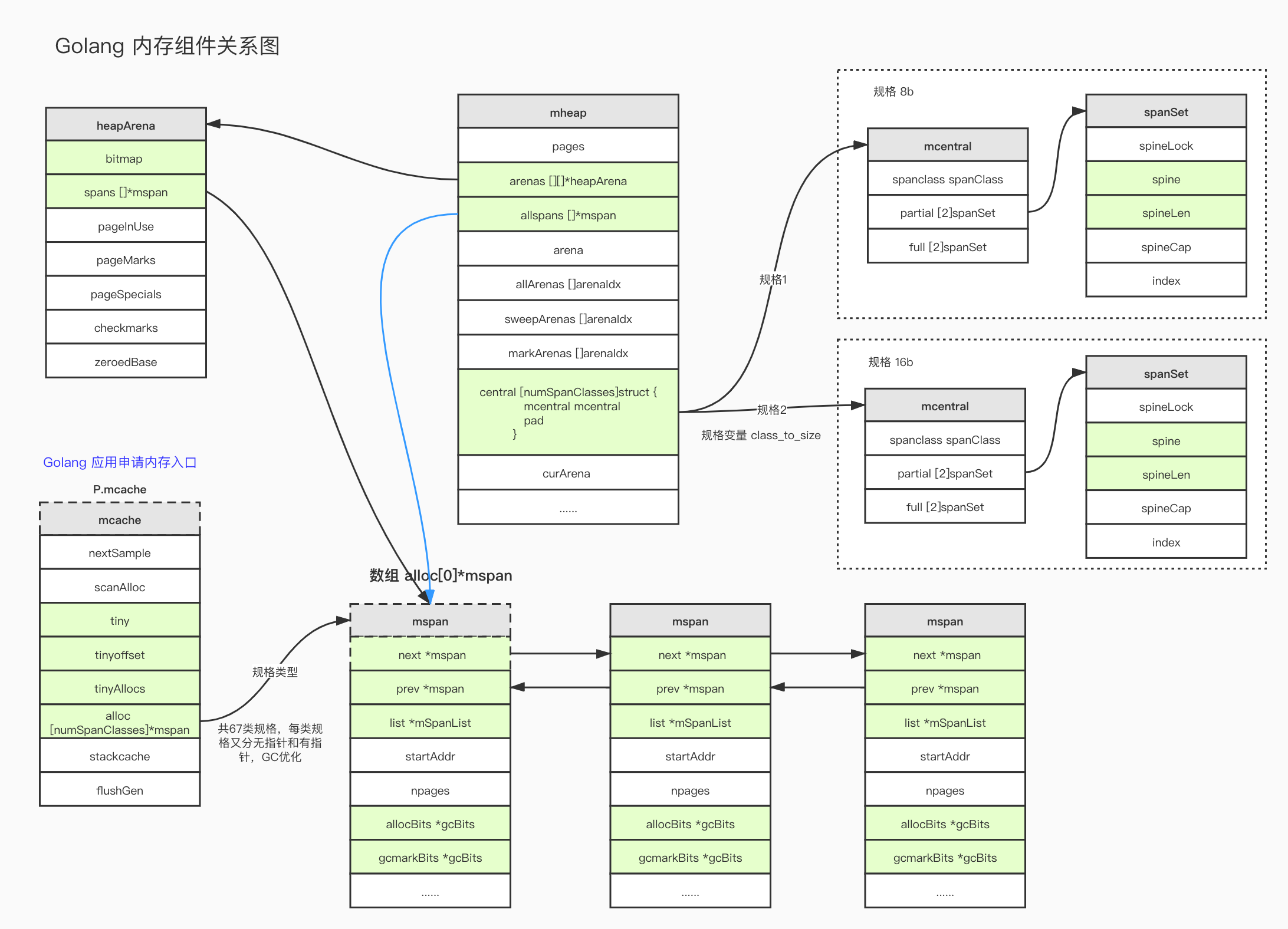 Golang 内存组件关系
Golang 内存组件关系