istio 中 sidecar 注入实现原理
admin
- 10 minutes read - 2128 words在 istio 中为了对流量进行有效的管理,一般通过注入的方式将代理 istio-proxy 与应用程序一起位于同一个Pod,然后通过 istio-init initContainer修改 iptables 实现 ingress 或 egress,那么在 istio 中这个注入是如何实现的呢,本节对其实现原理进行一些分析。
实现原理
在上一节《apiserver 中的webhook开发教程》 我们介绍过admission controller 基本实现原理,由此得知当创建一个资源对象的时候,可以通过定义 ValidatingWebhookConfiguration 或 MutatingWebhookConfiguration 实现在创建的进程中对这些 webhook 进行调用。而 MutatingWebhookConfiguration 则可以对请求的资源进行修改。在istio中的 injection 正是基于此原理实现的。
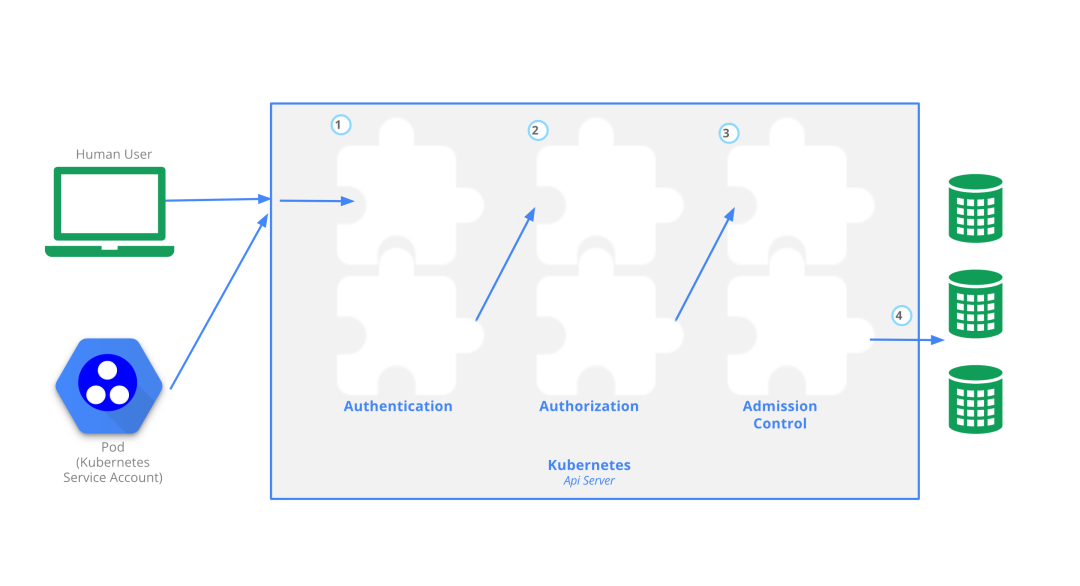
webhook配置
当我们在k8s集群中安装 istio 后,会创建一些资源,如 deployment、service、crd 等
$ istioctl install --set profile=demo -y
✔ Istio core installed
✔ Istiod installed
✔ Egress gateways installed
✔ Ingress gateways installed
✔ Installation complete
$ kubectl get deployment -n istio-system
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
istio-egressgateway 1/1 1 1 126m
istio-ingressgateway 1/1 1 1 126m
istiod 1/1 1 1 131m
$ kubectl get pod -n istio-system -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
istio-egressgateway-7b8b76f497-w2xvj 1/1 Running 0 139m 10.244.1.7 kind-worker <none> <none>
istio-ingressgateway-7f58d78f47-xfmd7 1/1 Running 0 139m 10.244.1.6 kind-worker <none> <none>
istiod-86b84db666-tj7c4 1/1 Running 0 144m 10.244.1.5 kind-worker <none> <none>
同时还为这些 deployment 创建对应的service
$ kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
istio-egressgateway ClusterIP 10.96.191.139 <none> 80/TCP,443/TCP 136m
istio-ingressgateway LoadBalancer 10.96.125.240 <pending> 15021:31434/TCP,80:30235/TCP,443:31254/TCP,31400:30109/TCP,15443:31055/TCP 136m
istiod ClusterIP 10.96.128.6 <none> 15010/TCP,15012/TCP,443/TCP,15014/TCP 141m
configMap
$ kubectl get cm istio-sidecar-injector -n istio-system
NAME DATA AGE
istio-sidecar-injector 2 4h33m
crd 资源
$ kubectl get crd -n istio-system
NAME CREATED AT
authorizationpolicies.security.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:29Z
destinationrules.networking.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:29Z
envoyfilters.networking.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:29Z
gateways.networking.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:30Z
istiooperators.install.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:30Z
peerauthentications.security.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:30Z
proxyconfigs.networking.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:30Z
requestauthentications.security.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:30Z
serviceentries.networking.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:30Z
sidecars.networking.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:30Z
telemetries.telemetry.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:30Z
virtualservices.networking.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:30Z
wasmplugins.extensions.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:30Z
workloadentries.networking.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:30Z
workloadgroups.networking.istio.io 2023-09-06T06:56:31Z
webhook 定义
$ kubectl get MutatingWebhookConfiguration -n istio-system
NAME WEBHOOKS AGE
istio-sidecar-injector 4 3h1m
$ kubectl get ValidatingWebhookConfiguration -n istio-system
NAME WEBHOOKS AGE
istio-validator-istio-system 1 155m
我们知道 MutatingWebhookConfiguration 准入 Webhook 会先被调用,它们可以修改发送到 API 服务器的对象以执行自定义的设置默认值操作。
在完成了所有对象修改并且 API 服务器也验证了所传入的对象之后,ValidatingWebhookConfiguration 的 Webhook 才会被调用,并通过拒绝请求的方式来强制实施自定义的策略。
这里声明了 四个MutatingWebhook 和 一个ValidatingWebhook
MutatingWebhookConfiguration
我们先看一下 MutatingWebhookConfiguration 的定义
$ kubectl get MutatingWebhookConfiguration -n istio-system -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
items:
- apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: MutatingWebhookConfiguration
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2023-09-06T06:56:32Z"
generation: 2
labels:
app: sidecar-injector
install.operator.istio.io/owning-resource: installed-state
install.operator.istio.io/owning-resource-namespace: istio-system
istio.io/rev: default
operator.istio.io/component: Pilot
operator.istio.io/managed: Reconcile
operator.istio.io/version: 1.19.0
release: istio
name: istio-sidecar-injector
resourceVersion: "302525"
uid: 971ca39e-e589-41ca-ad8a-480da90d7ea5
webhooks:
- admissionReviewVersions:
- v1beta1
- v1
clientConfig:
caBundle: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSLS0tLQo=
service:
name: istiod
namespace: istio-system
path: /inject
port: 443
failurePolicy: Fail
matchPolicy: Equivalent
name: rev.namespace.sidecar-injector.istio.io
namespaceSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: istio.io/rev
operator: In
values:
- default
- key: istio-injection
operator: DoesNotExist
objectSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: sidecar.istio.io/inject
operator: NotIn
values:
- "false"
reinvocationPolicy: Never
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
apiVersions:
- v1
operations:
- CREATE
resources:
- pods
scope: '*'
sideEffects: None
timeoutSeconds: 10
- admissionReviewVersions:
- v1beta1
- v1
clientConfig:
caBundle: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZEUtLS0tLQo=
service:
name: istiod
namespace: istio-system
path: /inject
port: 443
failurePolicy: Fail
matchPolicy: Equivalent
name: rev.object.sidecar-injector.istio.io
namespaceSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: istio.io/rev
operator: DoesNotExist
- key: istio-injection
operator: DoesNotExist
objectSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: sidecar.istio.io/inject
operator: NotIn
values:
- "false"
- key: istio.io/rev
operator: In
values:
- default
reinvocationPolicy: Never
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
apiVersions:
- v1
operations:
- CREATE
resources:
- pods
scope: '*'
sideEffects: None
timeoutSeconds: 10
- admissionReviewVersions:
- v1beta1
- v1
clientConfig:
caBundle: LS0tLS1CRUdJLQo=
service:
name: istiod
namespace: istio-system
path: /inject
port: 443
failurePolicy: Fail
matchPolicy: Equivalent
name: namespace.sidecar-injector.istio.io
namespaceSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: istio-injection
operator: In
values:
- enabled
objectSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: sidecar.istio.io/inject
operator: NotIn
values:
- "false"
reinvocationPolicy: Never
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
apiVersions:
- v1
operations:
- CREATE
resources:
- pods
scope: '*'
sideEffects: None
timeoutSeconds: 10
- admissionReviewVersions:
- v1beta1
- v1
clientConfig:
caBundle: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0UNBVEUtLS0tLQo=
service:
name: istiod
namespace: istio-system
path: /inject
port: 443
failurePolicy: Fail
matchPolicy: Equivalent
name: object.sidecar-injector.istio.io
namespaceSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: istio-injection
operator: DoesNotExist
- key: istio.io/rev
operator: DoesNotExist
objectSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: sidecar.istio.io/inject
operator: In
values:
- "true"
- key: istio.io/rev
operator: DoesNotExist
reinvocationPolicy: Never
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
apiVersions:
- v1
operations:
- CREATE
resources:
- pods
scope: '*'
sideEffects: None
timeoutSeconds: 10
kind: List
metadata:
resourceVersion: ""
这四个webhook 的 namespaceSelector 与objectSelector 配置都不一样,但请求规则是一样的,都是针对 pod 资源的 CREATE 操作。
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
apiVersions:
- v1
operations:
- CREATE
resources:
- pods
scope: '*'
同时请求服务端配置也是同一个
service:
name: istiod
namespace: istio-system
path: /inject
port: 443
也就是说只要满足这四个配置中的任何一项,就会发起对 webhook 的调用,然后服务端对其进行修改并返回 AdmissionReview 对象。
这里指定了
admissionReviewVersions支持的版本号,默认情况下会发送支持列表中的第一个版本号。
ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
再看一下 ValidatingWebhookConfiguration 的定义
$ kubectl get ValidatingWebhookConfiguration istio-validator-istio-system -o yaml -n istio-system
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2023-09-06T06:56:32Z"
generation: 3
labels:
app: istiod
install.operator.istio.io/owning-resource: installed-state
install.operator.istio.io/owning-resource-namespace: istio-system
istio: istiod
istio.io/rev: default
operator.istio.io/component: Pilot
operator.istio.io/managed: Reconcile
operator.istio.io/version: 1.19.0
release: istio
name: istio-validator-istio-system
resourceVersion: "302538"
uid: f1f0f788-bdba-4a72-81dc-72629547ffcf
webhooks:
- admissionReviewVersions:
- v1beta1
- v1
clientConfig:
caBundle: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCk1JSUMvRENDQWcxamJIVnpkLQo=
service:
name: istiod
namespace: istio-system
path: /validate
port: 443
failurePolicy: Fail
matchPolicy: Equivalent
name: rev.validation.istio.io
namespaceSelector: {}
objectSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: istio.io/rev
operator: In
values:
- default
rules:
- apiGroups:
- security.istio.io
- networking.istio.io
- telemetry.istio.io
- extensions.istio.io
apiVersions:
- '*'
operations:
- CREATE
- UPDATE
resources:
- '*'
scope: '*'
sideEffects: None
timeoutSeconds: 10
可以看到对 webhook 服务端地址定义
service:
name: istiod
namespace: istio-system
path: /validate
port: 443
从上面两个 webhook 的定义得知,它们请求目标为 istiod 这个 service ,请求路径为 /inject 和 /validate。
我们再看一下 istiod 服务的定义
$ kubectl get svc istiod -oyaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2023-09-06T06:56:32Z"
labels:
app: istiod
install.operator.istio.io/owning-resource: installed-state
install.operator.istio.io/owning-resource-namespace: istio-system
istio: pilot
istio.io/rev: default
operator.istio.io/component: Pilot
operator.istio.io/managed: Reconcile
operator.istio.io/version: 1.19.0
release: istio
name: istiod
namespace: istio-system
resourceVersion: "301216"
uid: 332c9a06-0b51-4fb0-af0f-0091d028c5ae
spec:
clusterIP: 10.96.128.6
clusterIPs:
- 10.96.128.6
internalTrafficPolicy: Cluster
ipFamilies:
- IPv4
ipFamilyPolicy: SingleStack
ports:
- name: grpc-xds
port: 15010
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 15010
- name: https-dns
port: 15012
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 15012
- name: https-webhook
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 15017
- name: http-monitoring
port: 15014
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 15014
selector:
app: istiod
istio: pilot
sessionAffinity: None
type: ClusterIP
status:
loadBalancer: {}
可以看到 service istiod 对应的pod(10.96.128.6),使用不同的端口提供了一些服务,如 grpc-xds(15010)、https-dns(15012)、http-monitoring(15014) 和 https-webhook(443),这里的 https-webhook 是上面提到过的 admission controller 服务端实现,其向外提供服务使用的是 443 端口,而对应容器的 15017 端口。
ValidatingWebhookConfiguration 不是本节关注的重点,所以我们才要关注 MutatingWebhookConfiguration 就可以了。
webhook 实现
上面我们知道了mutating webhook 的配置信息,执着我们再看一下它的服务端实现。
如果你不知道从哪里入手的话,不妨先看一下 istiod 容器使用的是哪一个镜像,然后根据 http://github.com/istio/istio 文档即可得到这个镜像对应的服务端代码。
$ kubectl describe pod/istiod-86b84db666-tj7c4 -n istio-system
Name: istiod-86b84db666-tj7c4
Namespace: istio-system
Priority: 0
Service Account: istiod
Node: kind-worker/172.18.0.3
Start Time: Wed, 06 Sep 2023 14:56:33 +0800
Labels: app=istiod
install.operator.istio.io/owning-resource=unknown
istio=pilot
istio.io/rev=default
operator.istio.io/component=Pilot
pod-template-hash=86b84db666
sidecar.istio.io/inject=false
Annotations: ambient.istio.io/redirection: disabled
prometheus.io/port: 15014
prometheus.io/scrape: true
sidecar.istio.io/inject: false
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.1.5
IPs:
IP: 10.244.1.5
Controlled By: ReplicaSet/istiod-86b84db666
Containers:
discovery:
Container ID: containerd://a465a4dc2ab329cd2a3f4230c586825dae049f9573488e2f16d0cdba5af415ea
Image: docker.io/istio/pilot:1.19.0
Image ID: docker.io/istio/pilot@sha256:d5132b1588c057121715d42ee33f85caeb9d3c1deff3e25730ac15a72af4465d
Ports: 8080/TCP, 15010/TCP, 15017/TCP
Host Ports: 0/TCP, 0/TCP, 0/TCP
...
可以看到这个Pod使用的镜像为 docker.io/istio/pilot:1.19.0 ,根据官方文档可知,其对应的 Dockerfile 为 https://github.com/istio/istio/blob/1.19.0/pilot/docker/Dockerfile.pilot,而其实现源码入口文件为 https://github.com/istio/istio/blob/1.19.0/pilot/cmd/pilot-discovery/main.go。
在/pilot/cmd 目录一共有两个子目录,其中一个是pilot-agent 目录,在上一节《istio之pilot-agent 源码分析》已对其进行了介绍。另一个是 pilot-discovery目录,这正是 istiod 核心功能代码实现位置。
先从入口函数开始
// pilot/cmd/pilot-discovery/app/cmd.go
func newDiscoveryCommand() *cobra.Command {
// 1. Create the server for the discovery service.
discoveryServer, err := bootstrap.NewServer(serverArgs)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to create discovery service: %v", err)
}
// 2. Start the server
if err := discoveryServer.Start(stop); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to start discovery service: %v", err)
}
}
在 bootstrap.NewServer() 函数里对webhook 服务进行了初始化
// pilot/pkg/bootstrap/server.go#L316-L329
func NewServer(args *PilotArgs, initFuncs ...func(*Server)) (*Server, error) {
...
// common https server for webhooks (e.g. injection, validation)
if s.kubeClient != nil {
s.initSecureWebhookServer(args)
wh, err := s.initSidecarInjector(args)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error initializing sidecar injector: %v", err)
}
s.readinessFlags.sidecarInjectorReady.Store(true)
s.webhookInfo.mu.Lock()
s.webhookInfo.wh = wh
s.webhookInfo.mu.Unlock()
if err := s.initConfigValidation(args); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error initializing config validator: %v", err)
}
}
...
}
在 s.initSecureWebhookServer() 函数里可以看到创建webhook的逻辑
func (s *Server) initSidecarInjector(args *PilotArgs) (*inject.Webhook, error) {
...
log.Info("initializing sidecar injector")
parameters := inject.WebhookParameters{
Watcher: watcher,
Env: s.environment,
Mux: s.httpsMux,
Revision: args.Revision,
}
// 创建 webhook
wh, err := inject.NewWebhook(parameters)
...
}
而在 NewWebhook() 函数里实现了对 /inject 服务的注册。
# /pkg/kube/inject/webhook.go
func NewWebhook(p WebhookParameters) (*Webhook, error) {
if p.Mux == nil {
return nil, errors.New("expected mux to be passed, but was not passed")
}
wh := &Webhook{
watcher: p.Watcher,
meshConfig: p.Env.Mesh(),
env: p.Env,
revision: p.Revision,
}
if p.KubeClient != nil {
if platform.IsOpenShift() {
wh.namespaces = kclient.New[*corev1.Namespace](p.KubeClient)
}
}
mc := NewMulticast(p.Watcher, wh.GetConfig)
mc.AddHandler(wh.updateConfig)
wh.MultiCast = mc
sidecarConfig, valuesConfig, err := p.Watcher.Get()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if err := wh.updateConfig(sidecarConfig, valuesConfig); err != nil {
log.Errorf("failed to process webhook config: %v", err)
}
// 注册注入服务
p.Mux.HandleFunc("/inject", wh.serveInject)
p.Mux.HandleFunc("/inject/", wh.serveInject)
p.Env.Watcher.AddMeshHandler(func() {
wh.mu.Lock()
wh.meshConfig = p.Env.Mesh()
wh.mu.Unlock()
})
return wh, nil
}
源码实现
func (wh *Webhook) serveInject(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
...
var reviewResponse *kube.AdmissionResponse
var obj runtime.Object
var ar *kube.AdmissionReview
if out, _, err := deserializer.Decode(body, nil, obj); err != nil {
handleError(fmt.Sprintf("Could not decode body: %v", err))
reviewResponse = toAdmissionResponse(err)
} else {
log.Debugf("AdmissionRequest for path=%s\n", path)
// 根据请求body创建 AdmissionReview 对象
ar, err = kube.AdmissionReviewKubeToAdapter(out)
if err != nil {
handleError(fmt.Sprintf("Could not decode object: %v", err))
reviewResponse = toAdmissionResponse(err)
} else {
// 注入
reviewResponse = wh.inject(ar, path)
}
}
response := kube.AdmissionReview{}
response.Response = reviewResponse
var responseKube runtime.Object
var apiVersion string
if ar != nil {
apiVersion = ar.APIVersion
response.TypeMeta = ar.TypeMeta
if response.Response != nil {
if ar.Request != nil {
response.Response.UID = ar.Request.UID
}
}
}
responseKube = kube.AdmissionReviewAdapterToKube(&response, apiVersion)
resp, err := json.Marshal(responseKube)
if err != nil {
log.Errorf("Could not encode response: %v", err)
http.Error(w, fmt.Sprintf("could not encode response: %v", err), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
if _, err := w.Write(resp); err != nil {
log.Errorf("Could not write response: %v", err)
http.Error(w, fmt.Sprintf("could not write response: %v", err), http.StatusInternalServerError)
}
}
注入逻辑
func (wh *Webhook) inject(ar *kube.AdmissionReview, path string) *kube.AdmissionResponse {
req := ar.Request
var pod corev1.Pod
if err := json.Unmarshal(req.Object.Raw, &pod); err != nil {
handleError(fmt.Sprintf("Could not unmarshal raw object: %v %s", err,
string(req.Object.Raw)))
return toAdmissionResponse(err)
}
// Managed fields is sometimes extremely large, leading to excessive CPU time on patch generation
// It does not impact the injection output at all, so we can just remove it.
pod.ManagedFields = nil
// Deal with potential empty fields, e.g., when the pod is created by a deployment
podName := potentialPodName(pod.ObjectMeta)
if pod.ObjectMeta.Namespace == "" {
pod.ObjectMeta.Namespace = req.Namespace
}
log.Infof("Sidecar injection request for %v/%v", req.Namespace, podName)
log.Debugf("Object: %v", string(req.Object.Raw))
log.Debugf("OldObject: %v", string(req.OldObject.Raw))
wh.mu.RLock()
if !injectRequired(IgnoredNamespaces.UnsortedList(), wh.Config, &pod.Spec, pod.ObjectMeta) {
log.Infof("Skipping %s/%s due to policy check", pod.ObjectMeta.Namespace, podName)
totalSkippedInjections.Increment()
wh.mu.RUnlock()
return &kube.AdmissionResponse{
Allowed: true,
}
}
proxyConfig := wh.env.GetProxyConfigOrDefault(pod.Namespace, pod.Labels, pod.Annotations, wh.meshConfig)
deploy, typeMeta := kube.GetDeployMetaFromPod(&pod)
params := InjectionParameters{
pod: &pod,
deployMeta: deploy,
typeMeta: typeMeta,
templates: wh.Config.Templates,
defaultTemplate: wh.Config.DefaultTemplates,
aliases: wh.Config.Aliases,
meshConfig: wh.meshConfig,
proxyConfig: proxyConfig,
valuesConfig: wh.valuesConfig,
revision: wh.revision,
injectedAnnotations: wh.Config.InjectedAnnotations,
proxyEnvs: parseInjectEnvs(path),
}
wh.mu.RUnlock()
// 注入Pod, 核心逻辑
patchBytes, err := injectPod(params)
if err != nil {
handleError(fmt.Sprintf("Pod injection failed: %v", err))
return toAdmissionResponse(err)
}
reviewResponse := kube.AdmissionResponse{
Allowed: true,
Patch: patchBytes,
PatchType: func() *string {
pt := "JSONPatch"
return &pt
}(),
}
totalSuccessfulInjections.Increment()
return &reviewResponse
}
函数 injectPod是注入逻辑的核心。这需要一个pod和注入模板,以及注入模板的一些输入,并生成一个 JSON Patch。
在webhook中我们将直接从Kubernetes收到一个Pod,并直接返回 补丁;Kubernetes将负责应用 补丁。
对于 kube-inject我们将从YAML中解析出一个Pod(可能涉及从更高级别的类型(如Deployment)中提取),然后在本地应用补丁。
注入逻辑的工作原理是首先在 input pod的顶部应用渲染的注入模板。这是使用战略性补丁合并完成的(https://github.com/kubernetes/community/blob/master/contributors/devel/sig-api-machinery/strategic-merge-patch.md)目前只支持单个模板,尽管将来要使用的模板将是可配置的,并且将通过按顺序应用多个模板来支持多个模板。
除了简单的模板之外,还有一些后期处理可以处理模板中无法覆盖的情况,例如重新排序pod、重写就绪探针等。
func injectPod(req InjectionParameters) ([]byte, error) {
checkPreconditions(req)
// The patch will be built relative to the initial pod, capture its current state
originalPodSpec, err := json.Marshal(req.pod)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// 1. Run the injection template, giving us a partial pod spec
// mergePod 指的是请求Pod被注入后的结果,而 templatePod 是指一个空的 Pod 被注入后的结果
mergedPod, injectedPodData, err := RunTemplate(req)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to run injection template: %v", err)
}
mergedPod, err = reapplyOverwrittenContainers(mergedPod, req.pod, injectedPodData)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to re apply container: %v", err)
}
// 2. Apply some additional transformations to the pod
if err := postProcessPod(mergedPod, *injectedPodData, req); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to process pod: %v", err)
}
// 3. 对比原始json 与 被修改后的json,生成 JSONPatch 对象
patch, err := createPatch(mergedPod, originalPodSpec)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create patch: %v", err)
}
log.Debugf("AdmissionResponse: patch=%v\n", string(patch))
return patch, nil
}
- 首先通过
RunTemplate()函数渲染sidecar模板内容, 返回值mergePod指的是请求Pod被注入后的结果,而templatePod是指一个空的 Pod 被注入后的结果。
func RunTemplate(params InjectionParameters) (mergedPod *corev1.Pod, templatePod *corev1.Pod, err error) {
...
mergedPod = params.pod
templatePod = &corev1.Pod{}
for _, templateName := range selectTemplates(params) {
// 读取注入模板( text/template 对象)
parsedTemplate, f := params.templates[templateName]
if !f {
return nil, nil, fmt.Errorf("requested template %q not found; have %v",
templateName, strings.Join(knownTemplates(params.templates), ", "))
}
// 传递模板数据,生成渲染结果
bbuf, err := runTemplate(parsedTemplate, data)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
// 合并 pod.spec,生成注入后的 pod
templatePod, err = applyOverlayYAML(templatePod, bbuf.Bytes())
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, fmt.Errorf("failed applying injection overlay: %v", err)
}
// 自定义注入情况,先移除已存在的注入容器
if features.EnableNativeSidecars.Get() &&
FindContainer(ProxyContainerName, templatePod.Spec.InitContainers) != nil &&
FindContainer(ProxyContainerName, mergedPod.Spec.Containers) != nil {
mergedPod = mergedPod.DeepCopy()
mergedPod.Spec.Containers, mergedPod.Spec.InitContainers = moveContainer(mergedPod.Spec.Containers, mergedPod.Spec.InitContainers, ProxyContainerName)
}
// 原始pod
mergedPod, err = applyOverlayYAML(mergedPod, bbuf.Bytes())
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, fmt.Errorf("failed parsing generated injected YAML (check Istio sidecar injector configuration): %v", err)
}
}
return mergedPod, templatePod, nil
}
postPorcessPod()是指将一些注入信息写在mergePod中,如 pod.Annotations 信息,同时将Pod中的容器进行重新排序。最后调用
createPatch()函数,生成 JSONPatch 作为mutating webhook的响应内容,然后APIServer应用此patch,并将最终的信息存在到etcd中。剩下的工作就是由 kubelet 来根据 Pod 信息在节点创建容器了。
注入方式
将 sidecar注入pod 有 namespace 自动 注入 和 手动注入 两种方式
namespace 自动注入
首先我们需要对namespace 启用注入
$ kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled
这里我们对名子空间 default 启用了自动注入功能,只需要添加 istio-injection=enabled 这个标记即可。
部署应用
$ kubectl apply -f deployment-nginx.yaml
这时将自动部署在启用自动注入的 default 名字空间内。
由于自动注入是在创建 Pod 的时候生成的,因此如果把namespace自动注入标签删除后,则原来创建的Pod是不会受到影响的。
取消namespace自动注入
$ kubectl label namespace default istio-injection-
此时原来创建的Pod仍处于注入状态,即使重复执行 kubectl apply -f deployment-nginx.yaml(配置文件未有任何改变) 命令。
手动注入
当在pod的命名空间中启用时,自动注入在pod创建时使用准入控制器(admission controller)注入代理配置。
如果要扫行手动注入,需执行命令
$ istioctl kube-inject -f deployment-nginx.yaml | kubectl apply -f -
先使用 istioctl kube-inject 命令进行配置注入修改,然后再 kubectl apply 应用结果。
总结
- Pod 注入发生在创建Pod的时候,因为在创建Pod的时候才会调用
mutating webhook。 - 当你对一个已存在的Pod进行注入的时候,其实会先创建原始Pod副本,等注入后的Pod创建完成后,再将原来的Pod删除,如命令
kubectl get deployment foo -o yaml | istioctl kube-inject -f - | kubectl apply -f - - pod是基于sidecar注入模板注入的,该模板在 istio-sidecar 注入器configmap中存储(
kubectl get cm -n istio-system istio-sidecar-injector -o yaml)。每个pod配置可用于覆盖单个pod上的这些选项。这是通过在pod中添加一个istio-proxy容器来完成的。sidecar注入将把这里定义的任何配置视为对默认注入模板的覆盖。另外还有了个网格配置configmap(kubectl -n istio-system get configmap istio -o yaml)
参考资料
- https://istio.io/latest/docs/setup/additional-setup/sidecar-injection/
- https://istio.io/latest/docs/setup/install/istioctl/
- https://kubernetes.io/zh-cn/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/extensible-admission-controllers/
- https://github.com/kubernetes/community/blob/master/contributors/devel/sig-api-machinery/strategic-merge-patch.md
- https://istio.io/latest/blog/2019/data-plane-setup/